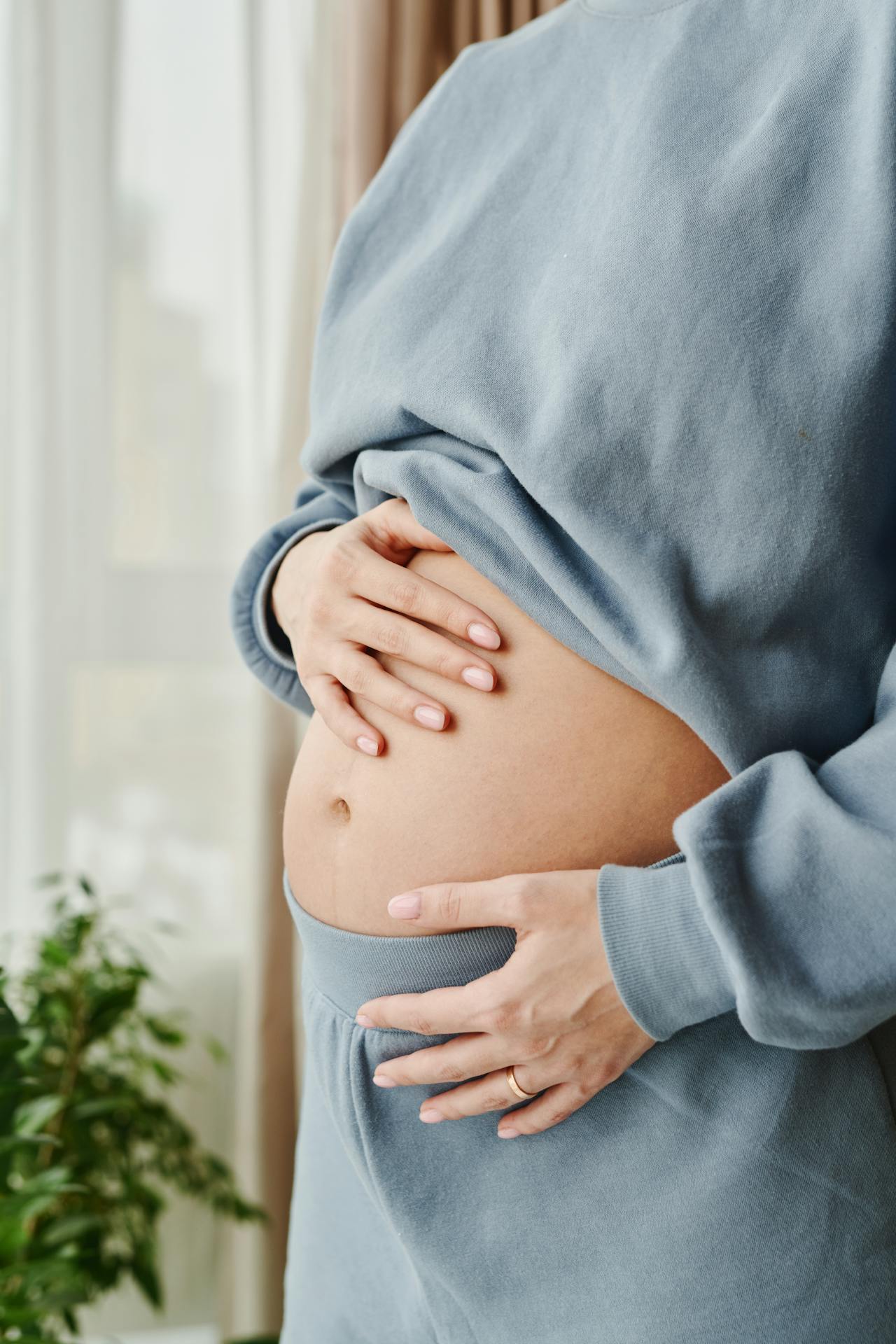

Understanding Morning Sickness in Pregnancy
Morning sickness, medically known as nausea and vomiting of pregnancy (NVP), is a common occurrence affecting the majority of pregnant women. While it’s often regarded as a sign of a healthy pregnancy, it can be a challenging experience for many women. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various aspects of morning sickness, including its causes, symptoms, risk factors, management strategies, and when to seek medical help.
Causes of Morning Sickness:
The exact cause of morning sickness is not fully understood, but it’s believed to be linked to hormonal changes occurring during pregnancy, particularly the increase in levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and estrogen. These hormonal fluctuations can affect the gastrointestinal system and the part of the brain responsible for regulating nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms of Morning Sickness:
Morning sickness typically presents as feelings of nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting. While it’s commonly experienced in the morning, symptoms can occur at any time of the day or night. Some women may also experience heightened sensitivity to certain smells or aversions to certain foods.
Risk Factors for Morning Sickness:
Several factors may increase the likelihood of experiencing morning sickness during pregnancy. These include:
- History of Morning Sickness: Women who have experienced morning sickness in previous pregnancies are more likely to experience it again.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes, particularly elevated levels of hCG and estrogen, play a significant role in the development of morning sickness.
- Multiparity: Women carrying multiple fetuses (e.g., twins or triplets) may experience more severe symptoms of morning sickness.
- Gastric Motility: Slowed gastric emptying during pregnancy can contribute to feelings of nausea and discomfort.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and emotional factors may exacerbate symptoms of morning sickness.
Management Strategies for Morning Sickness:
While morning sickness can be uncomfortable, several strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being:
- Dietary Modifications: Eating small, frequent meals throughout the day, avoiding spicy or greasy foods, and opting for bland, easily digestible snacks can help manage nausea.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential to prevent dehydration, particularly for women experiencing frequent vomiting. Sipping on water, herbal teas, or clear broths can help maintain fluid balance.
- Lifestyle Changes: Getting adequate rest, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, and minimizing exposure to strong odors or triggers can help reduce symptoms.
- Alternative Therapies: Some women find relief from morning sickness symptoms by using acupressure bands, aromatherapy, or consuming ginger supplements.
Medical intervention may be necessary for severe morning sickness or hyperemesis gravidarum (HG), a condition characterized by persistent vomiting, dehydration, and weight loss. Healthcare providers may prescribe anti-nausea medications or recommend hospitalization for intravenous fluids and nutritional support.
When to Seek Medical Help:
It’s essential for pregnant women to monitor their symptoms closely and seek medical attention if they experience:
- Severe or Prolonged Vomiting: Persistent vomiting that prevents adequate fluid intake and leads to dehydration.
- Weight Loss: Significant weight loss during pregnancy may indicate a more severe form of morning sickness, such as hyperemesis gravidarum.
- Signs of Dehydration: Symptoms of dehydration include dark urine, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and reduced urine output.
- Inability to Keep Food Down: If a pregnant woman is unable to tolerate any food or fluids for an extended period.
Overall, while morning sickness can be challenging to deal with, it’s essential to remember that it’s usually temporary and typically resolves on its own by the end of the first trimester. However, seeking support from healthcare providers and loved ones can help alleviate symptoms and ensure the well-being of both mother and baby throughout the pregnancy journey. Additionally, maintaining open communication with healthcare providers allows for timely intervention if symptoms become severe or persist beyond the first trimester. Remember, every pregnancy is unique, and while morning sickness may be a temporary discomfort for some, it’s crucial to prioritize self-care and seek assistance when needed to promote a healthy pregnancy experience for both the mother and the baby.









One Response
Hi! That is the worst part of pregnancy – vomiting. When I was pregnant, I vomit all day up to my 9th month. It was hard but it’s worth it after.